Setting up the Derivation of DTS Business Object Values
This chapter describes how to set up the derivation of business object values. You can perform this setup in the step Maintain business object preselection inputs or alternatively by double-clicking the business object input table in the step Maintain DTS objects. The business object values are stored in the business object table.
There are two modes for populating the business object table:
-
Manual: Allows you to enter the business object values manually via a simple ALV grid. The structure of the ALV grid represents the definition of the DTS business object. For example, the business object BUKRS (delivered in the content) has one column with the data element BUKRS (representing the company code). For a divestiture scenario at the company code level, the list of company codes delivered by the customer is used as the input to identify all other business object values – typically via automatic mode.
-
Automatic: Collects the business object values in the preselection based on the assigned derivation paths. In this case, an ALV grid with the following columns appears:
-
Input business object: Name of the source business object.
-
Path object: Name of the assigned derivation object. For more information, see the chapter DTS Derivation Path.
NOTE In edit mode, the buttons Create and
Create and  Delete are available in the toolbar to add or remove DTS derivation paths available for the selected business object. The search help (F4) offers only applicable paths that are defined in the DTS run ID.WARNING Adding or removing the derivation paths requires good application knowledge and has a major impact on the correctness of the transformation and the final consistency of the system.
Delete are available in the toolbar to add or remove DTS derivation paths available for the selected business object. The search help (F4) offers only applicable paths that are defined in the DTS run ID.WARNING Adding or removing the derivation paths requires good application knowledge and has a major impact on the correctness of the transformation and the final consistency of the system. -
Path type: Type of the DTS derivation path. For more information, see the chapter DTS Derivation Path.
-
Include: Flag indicating that the data collected by the derivation path is added to the results. See the diagrams below for more details.
-
Exclude: Flag indicating that the data collected by the derivation path is subtracted from the results. See the diagrams below for more details.
-
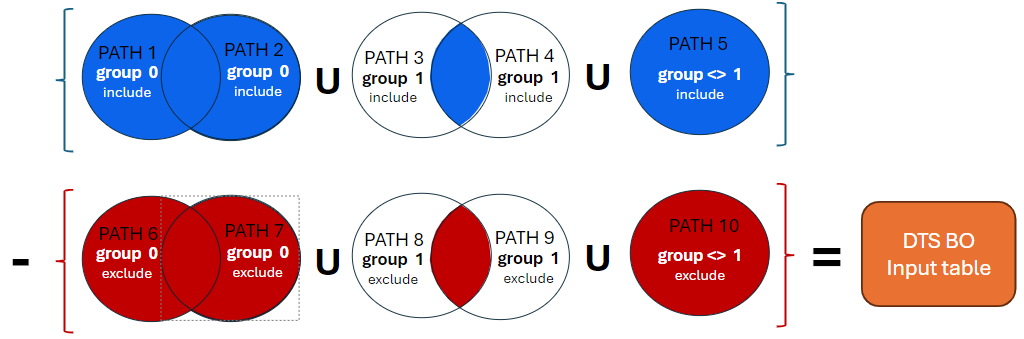
Input group: Defines the union or intersection among the processed derivation path results. The default value is 0 (union). Derivation paths with the same group that is above 0 are processed as an intersection. Any results collected among different groups are processed as a union. See the diagrams below for more details.
-
Direct business object update: Flag indicating that the data collected by the path is stored directly in the output business object table. The path table will be empty in this case. This option is editable only if exactly one path derives the output business object.
-
Output business object: Name of the business object where the collected values are stored.
The input group, include flag and exclude flag define how the values collected in the derivation path tables (circles) result in the output business object value table during the consolidation task execution. The paths from the same group are consolidated with following logic:
-
Tasks with the include flag are consolidated as first with union operation among different groups, into the included values
-
Then the exclude paths are consolidated as first with union operation among different groups, into the excluded values
-
At the end the excluded values are taken out from the list of the included values consolidated in the first two steps of the consolidation task.
The diagram with the set operations below shows an example of possible values consolidation for one business object with10 derivation paths. Following statements should help understand the processing:
-
If PATH5 would be part of the group 1, the result of PATH3, PATH 4 and PATH5 was 0 records due to disjunctive sets. Similarly for the exclusion paths 8, 9, 10.
-
If there is not overlap between include and exclude sets, only values from the include paths are considered.
-
Read the input group description from above.
-
The toolbar provides the following functions:
-
Save (Ctrl+S): Saves the screen.
-
Edit/display (Ctrl+F1): Switches between edit mode and display mode.
-
Check (Ctrl+F2): Checks the input consistency of all business objects. In case of an inconsistent setup, the generation of the preselection tasks ends with errors.
-
Mark as done (Shift+F1): Specifies that the scope setup is finished for this activity and that no further changes are expected. It also disables edit mode.
-
Setup > Undo mark as done: Reverses the Mark as done function.
-
Setup > Expert mode: Enables expert mode, in which all consistency checks are disabled. This is used only for content build purposes. Do not use this function in customer projects.